Welcome to another Tinto Talks, the final of four on the economy system for our secret game with the code name “Project Caesar”.
Today we will talk about all the things related to trade, including markets, merchants and trades. This talk is heavy on tooltip screenshots, and a lot of concepts to digest, so I recommend checking it through multiple times.
Markets
Let's start with the markets themselves. These are dynamic and will change through the playthrough, as countries can create new markets and disband their old if they so desire.
Each market has a center in a location, and the owner of that location is in control over that market.
Every location and coastal seazone will belong to the most fitting market, which depends on the market attraction of the market, the distance between the location and the market center, diplomatic factors, and more.
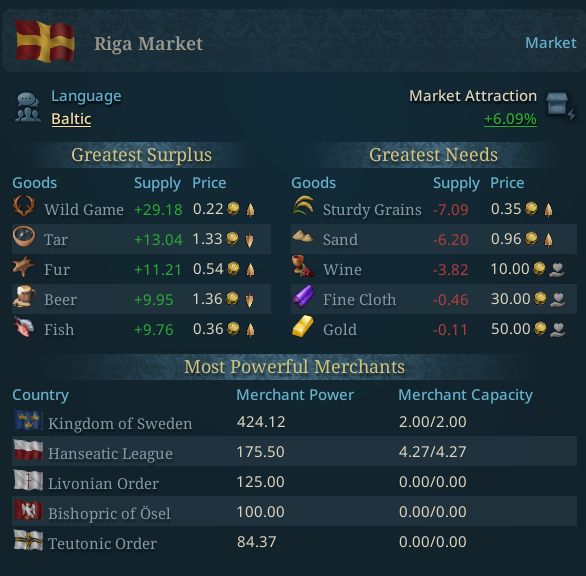
The Riga market has control over much of the Baltic region in the start..
A market has merchants, who have a power depending on buildings and maritime presence in the market, and a merchant capacity which depends on the infrastructure for trade that country has in that market. The Merchant Power impacts in which order exports from a market are executed, as there is not an endless supply of goods in a market. The Merchant Capacity impacts how much goods the merchants can ship.

This is the source of the Hanseatic League’s merchant capacity in Riga.
As you can see in the market screenshot, every good has a local price, and a supply vs demand value as well, let's take a look at the beer price in the next tooltip.
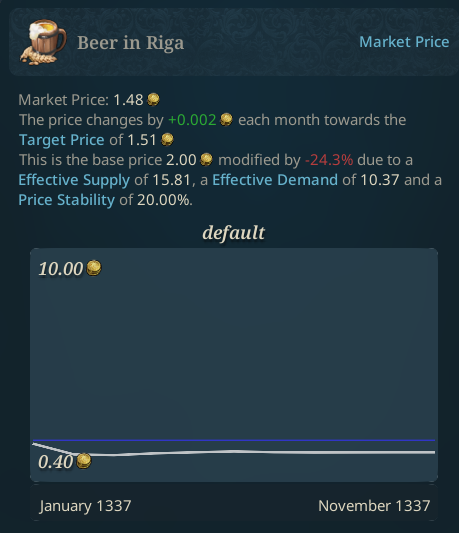
Cheap beer, must be paradise…
Prices change every month towards the Target Price, which depends on the supply and demand of the goods in the market, and the current price stability. Price stability can change through the ages as well.
Supply & Demand
The supply of each good in a market depends on several factors.
So what is ‘Base Production’? Some goods like clay, lumber, sand and stone are produced in every market, without the need for specific RGO’s, even if an RGO with that raw material can produce much more, and there are buildings that can be built to provide these as well.
Also, your burghers will trade on their own, if they have the capacity for it. They will attempt to address needs within the market, and can trade in a slightly shorter range, thus enriching their estate. There are laws and privileges that impact them, like the “Trade Monopolies” estate privilege that the Hanseatic League has granted in the earlier screenshot, which reduces their own merchant capacity by 25% to increase the capacity of the burghers by 100%
So what about demand? This is primarily from the maintenance, input, and construction of buildings, recruiting and maintaining armies and navies, and the demands of the population, but there are more sources as well.
Of course, trades themselves impact supply and demand as well.
Trade
You can use your merchant capacity in a market to either export a good from that market, or import a good from another market. Of course that market needs to be within your trade range, which is not world-spanning in 1337.
A trade is a variable amount of goods shipped from one market to another market, purchasing it for the local price in the exporting market. The longer the distance between the markets, the more capacity each good will require to ship, and higher the maintenance costs will be.
Trades have an impact on the last land location they are in before leaving the market, and the first one they enter in the importing market, giving boosts in development to them over time. A trade always has to trace a path on the map.
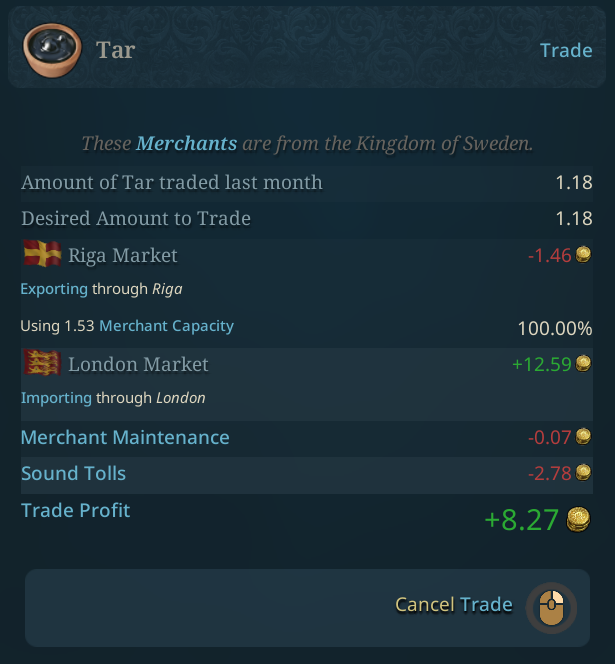
Our merchant power makes us get the amount of goods we want in Riga.
There are also the Sound Tolls, if you pass through Öresund or the Bosphorus to consider.
Diplomacy and Trade
There are many diplomatic factors that impact the trade and market mechanics of Project Caesar.
First of all, you can “Deny Market Access” to a nation owning a market, which will reduce the attraction of their markets on your locations, but also make anyone with merchants in those markets upset with you.
You can also request and/or offer market access preference making it likelier for a country’s locations to belong in a certain market.
If you dislike paying Sound Tolls, you can always try to ask for exemption for it through diplomacy with the country controlling the strait.
Some countries have isolated themselves completely, so you need to negotiate a specific exception to allow you to export or import from their markets.
There is also the possibility to embargo a country, which would block the merchants from that country to trade in your markets, and also to not be allowed to move through your country. Of course, this a legit casus belli, so use with care.
Other aspects to Trade
Each market can have specific goods banned for export or import, with one common example being that muslim markets will ban import and export of wine, beer and liquor.
We mentioned in an earlier Tinto Talks that Markets will have stockpiles, so that surplus can be stored for a rainy day. There are buildings that will increase the amount that can be stored.
There is also food in the markets, with prices adapting to the supply and demand of food as well.

Västra Götaland är Sveriges Kornbod!
There are also automation options where you can assign trading completely to the AI. You can also lock some trades so that the AI will not interfere with them.
Stay tuned, next week we’ll be talking about mercenaries, levies and regulars!
Today we will talk about all the things related to trade, including markets, merchants and trades. This talk is heavy on tooltip screenshots, and a lot of concepts to digest, so I recommend checking it through multiple times.
Markets
Let's start with the markets themselves. These are dynamic and will change through the playthrough, as countries can create new markets and disband their old if they so desire.
Each market has a center in a location, and the owner of that location is in control over that market.
Every location and coastal seazone will belong to the most fitting market, which depends on the market attraction of the market, the distance between the location and the market center, diplomatic factors, and more.
The Riga market has control over much of the Baltic region in the start..
A market has merchants, who have a power depending on buildings and maritime presence in the market, and a merchant capacity which depends on the infrastructure for trade that country has in that market. The Merchant Power impacts in which order exports from a market are executed, as there is not an endless supply of goods in a market. The Merchant Capacity impacts how much goods the merchants can ship.
This is the source of the Hanseatic League’s merchant capacity in Riga.
As you can see in the market screenshot, every good has a local price, and a supply vs demand value as well, let's take a look at the beer price in the next tooltip.
Cheap beer, must be paradise…
Prices change every month towards the Target Price, which depends on the supply and demand of the goods in the market, and the current price stability. Price stability can change through the ages as well.
Supply & Demand
The supply of each good in a market depends on several factors.
- The output from RGO’s
- The output from buildings
- Base Production
- Burgher Trades
So what is ‘Base Production’? Some goods like clay, lumber, sand and stone are produced in every market, without the need for specific RGO’s, even if an RGO with that raw material can produce much more, and there are buildings that can be built to provide these as well.
Also, your burghers will trade on their own, if they have the capacity for it. They will attempt to address needs within the market, and can trade in a slightly shorter range, thus enriching their estate. There are laws and privileges that impact them, like the “Trade Monopolies” estate privilege that the Hanseatic League has granted in the earlier screenshot, which reduces their own merchant capacity by 25% to increase the capacity of the burghers by 100%
So what about demand? This is primarily from the maintenance, input, and construction of buildings, recruiting and maintaining armies and navies, and the demands of the population, but there are more sources as well.
Of course, trades themselves impact supply and demand as well.
Trade
You can use your merchant capacity in a market to either export a good from that market, or import a good from another market. Of course that market needs to be within your trade range, which is not world-spanning in 1337.
A trade is a variable amount of goods shipped from one market to another market, purchasing it for the local price in the exporting market. The longer the distance between the markets, the more capacity each good will require to ship, and higher the maintenance costs will be.
Trades have an impact on the last land location they are in before leaving the market, and the first one they enter in the importing market, giving boosts in development to them over time. A trade always has to trace a path on the map.
Our merchant power makes us get the amount of goods we want in Riga.
There are also the Sound Tolls, if you pass through Öresund or the Bosphorus to consider.
Diplomacy and Trade
There are many diplomatic factors that impact the trade and market mechanics of Project Caesar.
First of all, you can “Deny Market Access” to a nation owning a market, which will reduce the attraction of their markets on your locations, but also make anyone with merchants in those markets upset with you.
You can also request and/or offer market access preference making it likelier for a country’s locations to belong in a certain market.
If you dislike paying Sound Tolls, you can always try to ask for exemption for it through diplomacy with the country controlling the strait.
Some countries have isolated themselves completely, so you need to negotiate a specific exception to allow you to export or import from their markets.
There is also the possibility to embargo a country, which would block the merchants from that country to trade in your markets, and also to not be allowed to move through your country. Of course, this a legit casus belli, so use with care.
Other aspects to Trade
Each market can have specific goods banned for export or import, with one common example being that muslim markets will ban import and export of wine, beer and liquor.
We mentioned in an earlier Tinto Talks that Markets will have stockpiles, so that surplus can be stored for a rainy day. There are buildings that will increase the amount that can be stored.
There is also food in the markets, with prices adapting to the supply and demand of food as well.
Västra Götaland är Sveriges Kornbod!
There are also automation options where you can assign trading completely to the AI. You can also lock some trades so that the AI will not interfere with them.
Stay tuned, next week we’ll be talking about mercenaries, levies and regulars!



